
Richard Feynman
Richard Feynman, greatest physicist of the twentieth century popular for his work in the field of quantum mechanics was born on May 11, 1918 in Queens New York. Due to his high intelligence and attractive approaches to the teaching, he has become one of the prominent figures in the field of physics.

The story of Richard Feynman shows that curiosity and critical thinking skills can go far. Isaac died in 1975, but his work in quantum mechanics and quantum electrodynamics was enough to get him a Nobel Prize and change the face of particle physics.
Super-intelligent and deeply inquisitive about the workings of the universe from childhood, Feynman knowingly or otherwise was on his way to becoming the genius he later became. His education path was MIT followed by Princeton University where he received Ph. D. in physics in order to build a future full of important scientific discoveries.

Quantum mechanics was one of the main directions in which Feynman worked throughout his career resulting in establishing the Feynman diagrams. In this way, diagrams have become a basic concept in theoretical physics that has irrevocably altered the nature of the field.
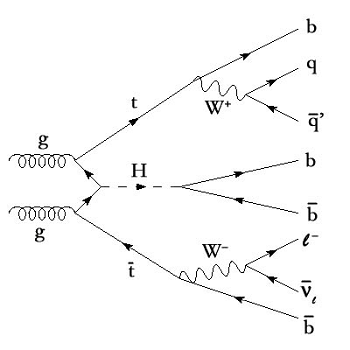
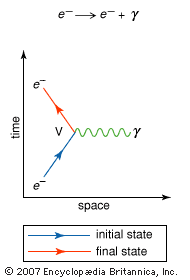
Although Feynman was mainly involved in solving terrestrial physics problems, his capacity to analyze space shuttle challenger disaster in 1986 showed that he could couch his expertise in space-related problems to give insights on the technological mishaps that culminated to the disaster.
Feynman was accorded many awards for his talent such as the Albert Einstein Award and Oersted Medal. This is why his election to the National Academy of Sciences reflected the he had made to the contributors of science.
Feynman had a rather eventful life illuminative of his idiosyncrasies, offbeat and unconventional tutoring style. His autobiographical writings are about the cheerful life of a man-of-geniuses, who could find a subject for happiness in bongo drumming or translating Mayan hieroglyphs.
This work of Richard Feynman will remain a priority in the annals of science for many years to come. His theoretical physics discoveries will remain a motivation to scientists and learners, and it signifies that his impact on the academic world will remain significant.